03 Feb 2026
Rhinoplasty Revision Surgery in Mohali: Cost When Your First Nose Job Fails

Dr. Harinder K Bali
17 Nov 2025
Call +91 80788 80788 to request an appointment.
At Livasa Hospitals, Livasa Amritsar, we provide advanced cardiac electrophysiology services for patients with heart failure, arrhythmias, and cardiac device needs. This comprehensive guide explains what heart failure is, how electrophysiology (EP) specialists diagnose rhythm problems, and when pacemakers, ICDs, or CRT-D devices are recommended. Whether you are researching heart failure treatment in Amritsar Punjab or exploring options for pacemaker surgery Amritsar, this article will help you understand symptoms, tests, procedural details, follow-up care, and cost considerations specific to Punjab and Amritsar.
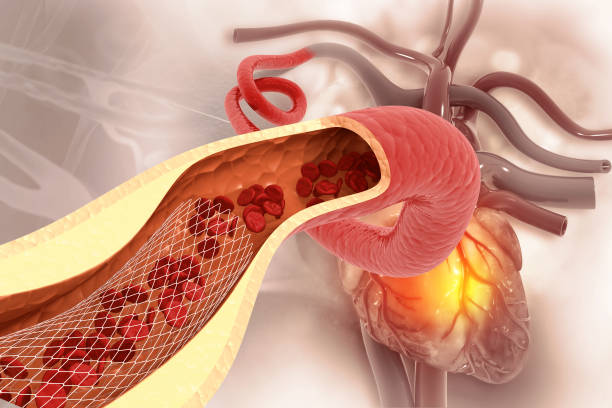
Heart failure is not a single disease but a clinical syndrome in which the heart cannot pump blood effectively to meet the body's needs. It can result from weakened heart muscle (systolic dysfunction), stiff heart muscle (diastolic dysfunction), valvular disease, or long-standing arrhythmias. Electrophysiology is a cardiology sub-specialty that focuses on the heart's electrical system. An electrophysiologist diagnoses and treats rhythm disorders and manages implantation of electrical devices such as pacemakers, automated implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (AICD/ICD), and cardiac resynchronization therapy defibrillators (CRT-D). In Amritsar and across Punjab, the prevalence of heart failure is rising due to increased longevity, diabetes, hypertension, and coronary artery disease. Globally, it is estimated that over 64 million people live with heart failure. In India, cardiovascular diseases account for nearly 28% of deaths, and heart failure constitutes a significant portion of hospital admissions for cardiac conditions.
Electrophysiology combines diagnostic tools — like electrocardiograms (ECG), Holter monitoring, event recorders, and invasive EP studies — with therapeutic procedures including ablation and device implantation. For patients in Amritsar looking for the best electrophysiology hospital in Punjab or the arrhythmia specialist Punjab trusts, Livasa Amritsar provides a dedicated EP lab, experienced electrophysiologists, and a multidisciplinary heart failure team to plan personalized care. Early referral to an EP specialist is particularly important for people with symptomatic arrhythmias, recurrent syncope, or progressive heart failure symptoms despite medication.
Heart failure occurs when structural or functional heart abnormalities impair ventricular filling or ejection of blood. Causes vary and can be grouped broadly into ischemic and non-ischemic categories. Ischemic heart disease (coronary artery disease) is the most common cause worldwide; repeated heart attacks can damage heart muscle and lead to chronic heart failure. Other causes include long-standing hypertension, cardiomyopathies (dilated, hypertrophic, restrictive), valvular diseases, congenital heart disease, infections such as myocarditis, metabolic diseases, and toxic exposures (alcohol, chemotherapy).
Heart failure is commonly classified by:
In Punjab, lifestyle factors such as high rates of diabetes and hypertension are significant contributors to the growing burden of heart failure. A regional focus on control of blood pressure, blood sugar, and coronary risk factors is essential to reduce new cases. For patients in Amritsar, early involvement of a heart failure specialist in Punjab enables a comprehensive plan combining medicines, device therapy when indicated, and lifestyle modifications.
Recognizing heart failure early improves outcomes. Symptoms often progress gradually and can be mistaken for aging or other conditions, but timely evaluation is crucial. Common symptoms include:
Seek urgent care if you experience sudden severe breathlessness, fainting (syncope), chest pain, or rapid worsening of symptoms. These may signal acute decompensated heart failure, severe arrhythmias, or ischemia. In Amritsar and Punjab, patients who experience such symptoms should contact a hospital with an electrophysiology and heart failure program. Livasa Hospitals, Livasa Amritsar offers emergency evaluation and a pacemaker emergency service Amritsar for immediate device-related concerns or symptomatic bradyarrhythmias.
Because arrhythmias can both cause and result from heart failure, symptoms such as unexplained palpitations, dizziness, or syncope should prompt referral to an arrhythmia specialist Punjab or an electrophysiologist Amritsar. Early diagnosis helps prevent complications and allows timely consideration of pacemaker, ICD implantation, or CRT-D therapy when indicated.
Comprehensive diagnosis begins with a thorough history and physical examination, followed by targeted investigations to assess cardiac structure, function, and electrical stability. An electrophysiology-focused center such as the cardiac electrophysiology center in Punjab will typically perform:
These tests help the multidisciplinary team at Livasa Amritsar decide whether a patient will benefit from medical therapy alone, targeted catheter ablation for arrhythmias, or device implantation such as a pacemaker, ICD, or CRT-D. The combination of non-invasive and invasive assessments optimizes outcomes and personalizes therapy according to the patient's rhythm, ventricular function, and risk of sudden cardiac death.
Cardiac devices restore and protect heart rhythm and function. Understanding their purpose helps patients make informed decisions. The main device types are:
Device selection depends on underlying rhythm disorder, ejection fraction, symptoms, and risk factors. For example, a patient with symptomatic bradycardia will typically need a pacemaker, while one with EF ≤35% and ventricular tachycardia risk may benefit from an ICD. Patients with heart failure and wide QRS (usually left bundle branch block) may derive significant improvement in symptoms and survival from CRT-D or CRT-P (pacer without defibrillator).
At Livasa Amritsar the electrophysiology team evaluates each patient for the most appropriate device and explains advantages and trade-offs — including the option of a biventricular pacemaker for resynchronization or a leadless pacemaker where suitable. For Amritsar residents searching for pacemaker implantation hospital Amritsar or the best pacemaker hospital in Punjab, device expertise, an experienced implant team, and an established device clinic Punjab for follow-up are key considerations.
Patients often ask how pacemakers, ICDs, CRT, and leadless systems compare. Below is a clear comparison to help explain benefits, risks, and typical recovery expectations. This table assists patients and families in understanding differences and setting realistic expectations for post-procedure life.
| Procedure type | Benefits | Recovery time | Primary risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Permanent pacemaker (single/dual) | Restores adequate heart rate, reduces syncope, improves symptoms | 1–2 weeks for full activity; hospital stay 24–48 hrs | Infection, lead displacement, bleeding, pocket hematoma |
| Leadless pacemaker | No leads; lower risk of lead-related complications; smaller pocket | Usually same-day or 24-hour discharge; rapid recovery | Vascular access issues, device retrieval challenges if needed |
| ICD implantation | Prevents sudden cardiac death by terminating dangerous ventricular arrhythmias | 1–2 weeks for activity restrictions; hospital stay 1–3 days | Inappropriate shocks, infection, lead issues |
| CRT-D / CRT-P (biventricular) | Improves symptoms, exercise tolerance, and survival in select heart failure patients | 2–4 weeks for full recovery; hospital stay 1–3 days | Lead placement difficulties, infection, pocket complications |
Device therapy requires informed consent and discussion of long-term considerations: battery longevity (replacement every 5–12 years depending on device and usage), travel and workplace implications, and follow-up schedules. Livasa Amritsar maintains a dedicated pacemaker clinic Amritsar and device clinic Punjab to manage programming, remote monitoring, and troubleshooting.
Device implantation is usually performed in a sterile operating theatre or cath lab under local anesthesia with sedation. Pre-procedure evaluation includes blood tests, imaging, and sometimes temporary pacing if the patient is unstable. Key steps include:
Most patients stay overnight for monitoring; complex CRT or ICD implants may require a longer stay. After discharge, activity restrictions (no heavy lifting for several weeks, arm movement limitations) protect the lead-pocket and lower the chance of displacement. Livasa Hospitals provides clear discharge instructions, and a follow-up plan in the pacemaker follow up clinic Amritsar or via remote monitoring where available.
Successful device therapy depends on careful follow-up. Livasa Amritsar operates a structured device clinic Amritsar to provide routine checks, programming adjustments, and patient education. Typical follow-up schedule:
Education topics covered by the pacemaker clinic Punjab include travel advice, MRI compatibility, precautions around electrical interference, and guidance on activities like driving. Device clinics also coordinate care with heart failure specialists to ensure medications (ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists, SGLT2 inhibitors) and device therapy together provide optimal outcomes. For Amritsar residents, Livasa Hospitals offers accessible follow-up and emergency device services so patients can feel secure close to home.
Cost is an important factor in decision-making for device therapy. Prices vary by device type, hospital infrastructure, surgeon and cardiologist fees, and length of stay. Below is a comparative table showing typical cost ranges in Punjab/Amritsar to help with planning. These are indicative ranges and can vary based on device brand, model (CRT-D vs CRT-P), and individual clinical needs. For precise estimates contact Livasa Amritsar at +91 80788 80788 or use the appointment link.
| Procedure | Typical cost range (Amritsar, Punjab) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Permanent pacemaker (single/dual) | INR 60,000 – 2,50,000 | Dependent on single vs dual chamber and brand |
| Leadless pacemaker | INR 2,50,000 – 6,00,000 | Higher device cost but shorter hospital stays |
| ICD implantation | INR 3,00,000 – 8,00,000 | Higher for dual-lead and shock-capable devices |
| CRT-P / CRT-D | INR 4,00,000 – 10,00,000 | CRT-D costs more due to integrated defibrillator function |
Financing options, insurance coverage, and government schemes (Ayushman Bharat, employer insurance) can substantially reduce out-of-pocket expenses. Livasa Hospitals supports patients with billing counseling and insurance coordination. For exact pricing, ask for a personalized cost estimate for pacemaker implant cost Amritsar or CRT-D implantation cost Amritsar when you book an appointment at Livasa Amritsar via https://www.livasahospitals.com/appointment or call +91 80788 80788.
Selecting a centre for heart failure and device therapy should involve evaluating expertise, infrastructure, and continuity of care. Key factors to consider include:
Livasa Hospitals in Amritsar meets these criteria with a state-of-the-art EP lab, experienced electrophysiologist Amritsar team, and a dedicated heart failure clinic Amritsar. For residents searching “pacemaker implantation near me Amritsar” or “best electrophysiologist in Amritsar,” Livasa offers comprehensive pre-procedure counseling, transparent cost discussions, and coordinated post-discharge care. You can schedule a consultation online at https://www.livasahospitals.com/appointment or call +91 80788 80788 to speak with an expert.
Preventing heart failure progression and optimizing outcomes after device implantation requires a combination of medication adherence, lifestyle changes, and regular follow-up. Key recommendations:
Living with a pacemaker or ICD often allows patients to return to normal activities and enjoy improved symptoms. Regular visits to the pacemaker follow up clinic Amritsar or remote device monitoring ensure early detection of issues and timely device reprogramming. For regional prevention efforts in Punjab, community screening for hypertension, diabetes, and early cardiac evaluation can reduce the incidence of heart failure and the future need for device therapy.
Many patients have similar questions before undergoing device therapy. Below are common FAQs with clear answers to help guide decisions.
If you or a loved one in Amritsar or Punjab experiences symptoms of heart failure or arrhythmias, the next step is a specialist consultation. Book an appointment with Livasa Hospitals, Livasa Amritsar at https://www.livasahospitals.com/appointment or call +91 80788 80788. Our team will arrange diagnostic testing, discuss device options (including leadless pacemaker Amritsar and CRT-D Amritsar), and provide personalized care planning.
At Livasa Hospitals, Livasa Amritsar, our electrophysiology and heart failure teams partner with you to choose the safest, most effective treatment plan. Whether you need heart failure treatment Punjab, pacemaker surgery Punjab, or long-term device follow-up, we offer advanced technology and compassionate care.
Call us at +91 80788 80788 or book an appointment online to speak with an electrophysiologist or heart failure specialist at Livasa Amritsar.
Rhinoplasty Revision Surgery in Mohali: Cost When Your First Nose Job Fails
Plastic Surgery After Massive Weight Loss: Body Contouring Packages in Mohali
ENT + Cosmetic in Mohali: Septoplasty for Breathing with Cosmetic Rhinoplasty Offers
Livasa Healthcare Group Corporate Office,Phase-8, Industrial Area, Sector 73, Sahibzada Ajit Singh Nagar, Punjab 160071
| Mohali | +91-99888 23456 |
| Amritsar | +91-99887 49494 |
| Hoshiarpur | +91-99883 35353 |
| Nawanshahr | +91-75081 82337 |
| Khanna | +91-98888 05394 |