27 Feb 2026
Why Choose Livasa Mohali for Brain & Spine Surgery in Chandigarh Tricity?


Dr. Pradeep Kumar Sharma
04 Feb 2025
Call +91 80788 80788 to request an appointment.
The human brain, one of the most intricate and powerful organs, is known for its exceptional memory capacity, which allows us to store and recall vast amounts of information. This incredible ability supports everything from remembering everyday tasks to preserving lifelong knowledge and experiences. In this article, we delve into the memory capacity of the human brain, exploring how memory works, the estimated storage potential, types of memory, and factors that influence memory performance.
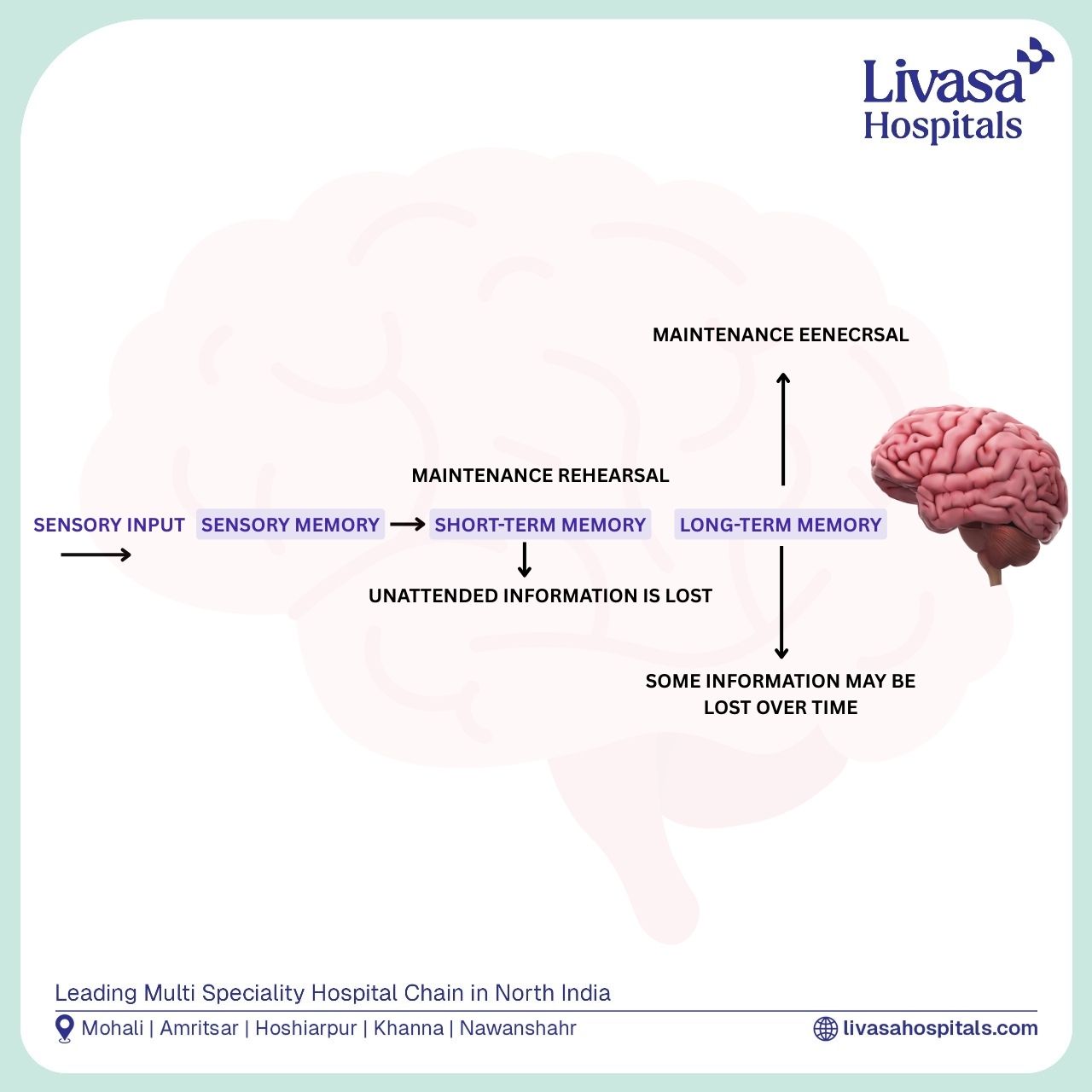
Memory is a complex cognitive function that involves encoding, storing, and retrieving information. These three critical stages include:
Encoding: Initial transformation of sensory inputs like sights and sounds into storable data, heavily influenced by attention.
Storage: Memories are stored in three main forms:
Sensory Memory — fleeting impressions lasting seconds.
Short-Term Memory (STM) — temporary storage for seconds to minutes.
Long-Term Memory (LTM) — durable storage that can last a lifetime.
Retrieval: Accessing stored information, often dependent on how well memories were encoded and stored.
Estimating the memory capacity of the human brain is complex due to the brain’s unique structure. Neuroscientists often compare this capacity to computer storage for perspective. The brain contains roughly 86 billion neurons, each forming thousands of synapses, which function as data storage points. Current estimates suggest the brain can hold about 2.5 petabytes of information — approximately 2.5 million gigabytes or 300 years of continuous video recordings.
Unlike a computer’s fixed storage, the brain distributes memories across vast neural networks, providing efficiency and resilience.
Memory can be divided into two primary categories:
Explicit Memory (Declarative): Conscious memories including facts (semantic memory) and personal events (episodic memory).
Implicit Memory (Non-Declarative): Unconscious memories involved in skills like riding a bike or typing.
Several elements impact memory function and capacity, including:
Age: Memory tends to decline naturally with aging.
Health: Disorders like Alzheimer’s affect memory negatively.
Lifestyle: Adequate sleep, nutrition, and regular exercise improve memory.
Emotions: Strong emotions can enhance memory encoding.
While the brain’s memory capacity is vast, limitations exist, as forgetting helps clear irrelevant information. To maximize your memory potential:
Practice repetition to strengthen neural connections.
Maintain mindfulness and reduce distractions during learning.
Engage in brain training activities such as puzzles and new skill acquisition.
Follow a healthy lifestyle to support cognitive health.
The astonishing memory capacity of the human brain allows us to manage countless experiences and information. Although science continues to unlock its full potential, understanding how memory works helps us appreciate the remarkable nature of this vital organ.
Why Choose Livasa Mohali for Brain & Spine Surgery in Chandigarh Tricity?
Slip Disc & Sciatica Treatment in Mohali: Surgery vs Non-Surgical Options & Cost
Head Injury & Brain Trauma Management in Mohali: CT Scan, Surgery & ICU Cost
Livasa Healthcare Group Corporate Office,Phase-8, Industrial Area, Sector 73, Sahibzada Ajit Singh Nagar, Punjab 160071
| Mohali | +91-99888 23456 |
| Amritsar | +91-99887 49494 |
| Hoshiarpur | +91-99883 35353 |
| Nawanshahr | +91-75081 82337 |
| Khanna | +91-98888 05394 |