03 Feb 2026
Rhinoplasty Revision Surgery in Mohali: Cost When Your First Nose Job Fails


Dr. Apurwa Bardhan
30 Jan 2025
Call +91 80788 80788 to request an appointment.
Polycystic Ovary Disease (PCOD) and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) are two common conditions affecting women’s reproductive health. Although their names sound similar and share overlapping symptoms, they are distinct in their causes, manifestations, and long-term health implications. Understanding the key differences between PCOD and PCOS can help women take proactive steps toward managing their health.
What is PCOD?
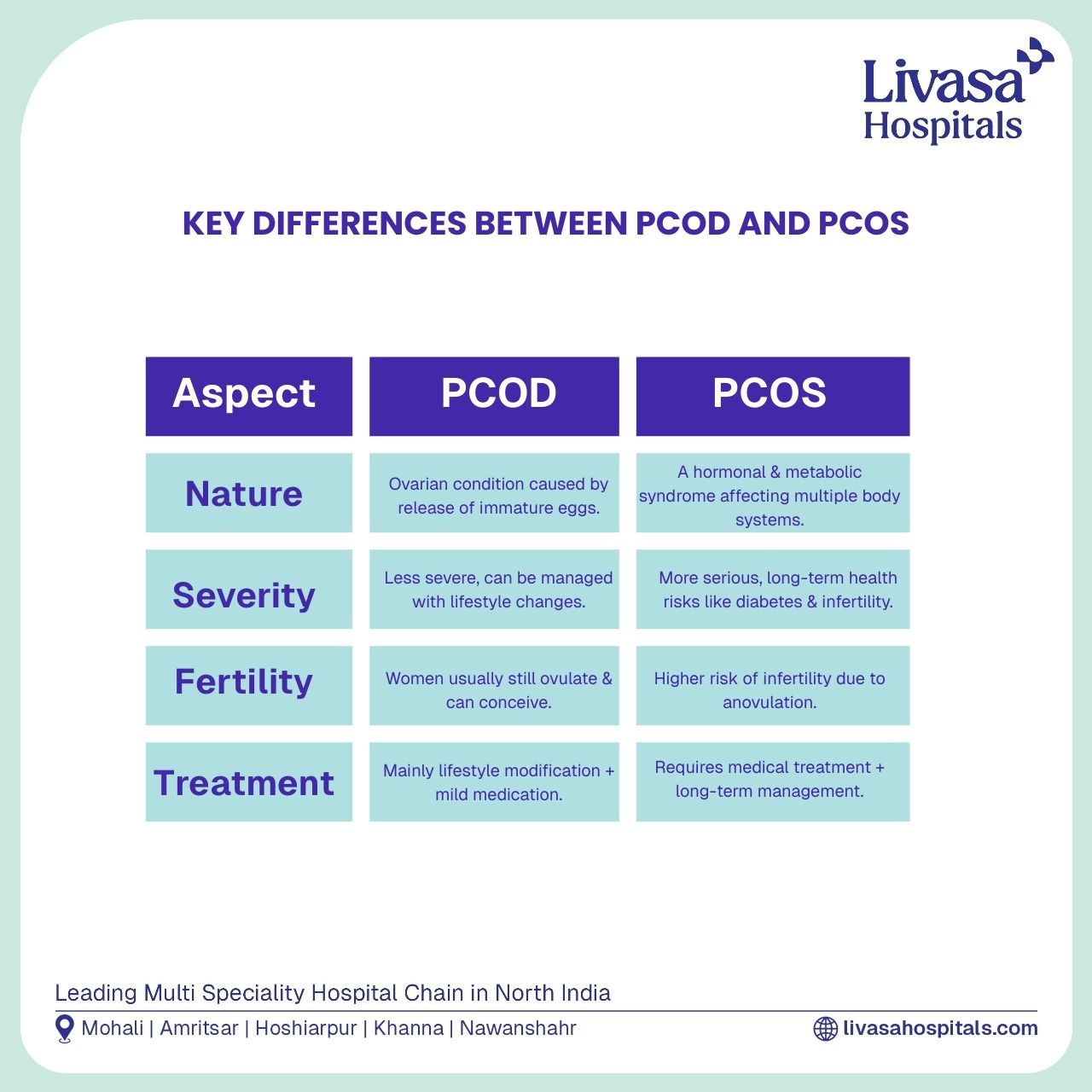
Polycystic Ovary Disease (PCOD) is a condition in which the ovaries contain a large number of immature or partially mature follicles that are unable to release eggs properly. These follicles can accumulate and form cysts. In PCOD, the ovaries may be enlarged, and there may be an imbalance in hormone levels. However, women with PCOD may still have normal hormone levels and regular menstrual cycles.
PCOD is generally considered a milder condition compared to PCOS. It can often be managed with lifestyle changes, including a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management. Treatment may also include hormonal medications, but it rarely leads to serious complications in the long term.
What is PCOS?
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a more complex hormonal disorder that involves a combination of symptoms related to an imbalance of sex hormones, particularly high levels of androgens (male hormones). Women with PCOS may experience irregular or absent periods, difficulty in ovulation, and infertility issues. In addition, they may develop cysts in the ovaries, though cysts themselves do not define PCOS.
PCOS often leads to more significant health challenges than PCOD, including weight gain, insulin resistance, acne, excessive hair growth (hirsutism), and thinning hair. The condition can also lead to long-term complications such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and endometrial cancer if left untreated.
Key Differences Between PCOD and PCOS
Which is More Severe?
PCOS is generally considered more severe than PCOD due to its potential long-term health complications. While both conditions can lead to fertility issues, PCOS is associated with a higher risk of developing metabolic disorders such as insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and obesity. It can also increase the risk of cardiovascular problems and endometrial cancer.
Women with PCOS may experience more pronounced symptoms, which can significantly impact their quality of life. These include severe acne, unwanted facial hair, and scalp hair thinning. Additionally, untreated PCOS can lead to infertility, making timely medical intervention essential for managing the condition.
PCOD, on the other hand, tends to be less severe and more easily managed. Most women with PCOD do not experience the same degree of hormonal imbalance or the same risk of developing metabolic disorders. With lifestyle modifications and medications when necessary, women with PCOD can typically lead healthy, normal lives.
Conclusion
Both PCOD and PCOS are common conditions, but they differ in their severity and long-term health consequences. PCOS is generally more severe due to its potential for causing metabolic disorders, fertility issues, and other complications. However, both conditions can be managed effectively with the right treatment and lifestyle changes. If you suspect you may have either condition, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan. Early intervention can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the risk of complications, ensuring better reproductive and overall health.
Rhinoplasty Revision Surgery in Mohali: Cost When Your First Nose Job Fails
Plastic Surgery After Massive Weight Loss: Body Contouring Packages in Mohali
ENT + Cosmetic in Mohali: Septoplasty for Breathing with Cosmetic Rhinoplasty Offers
Livasa Healthcare Group Corporate Office,Phase-8, Industrial Area, Sector 73, Sahibzada Ajit Singh Nagar, Punjab 160071
| Mohali | +91-99888 23456 |
| Amritsar | +91-99887 49494 |
| Hoshiarpur | +91-99883 35353 |
| Nawanshahr | +91-75081 82337 |
| Khanna | +91-98888 05394 |